Nickel Coating Technology – Nickel is a metal which lends itself to the electroless plating methods employed by MTL for particle coating. It has the potential to be used in a number of application areas, not least as a cheaper alternative to conductive silver.
However, in this particular application, nickel demonstrates gradual surface ‘passivation’ and the level of conductivity decays over a relatively short time. This may be an issue which could be resolved through further development work.
Nickel coated hollow glass microspheres also have ferromagnetic properties, which MTL has investigated with respect to their use in low density materials for radar absorption. Unfortunately, the frequency bands of interest in ‘stealth’ applications are not strongly absorbed by the nickel composites prepared using MTL materials. This application may be better served by the iron coating technology developed by MTL .
There could be potential in the use of light weight cores coated with relatively thick nickel layers e.g. up to 10 microns. These materials could be used in inductive heating applications where the relatively low thermal mass of the coated low density core would be of advantage in rapid temperature cycling. Opportunities still exist in this area and MTL have established methods for the preparation of coated particles of the necessary specification.
From:microspheretechnology
Posted by admin on February 24, 2016 at 2:36 am under Hollow Glass Microspheres.
Comments Off on Nickel Coating Technology.
These hollow glass microspheres offer a variety of advantages over conventional irregularly-shaped mineral fillers or glass fiber.
Can improve fuel economy.
From:3M
Posted by admin on February 18, 2016 at 5:55 am under glass bubble, Hollow Glass Microspheres.
Comments Off on Glass Bubbles for Transportation.
Researchers from Carnegie Melon University and Karlsruhe Institute of Technology have recently published an article in Journal of the Royal Societytitled Staying Sticky: Contact Self-Cleaning of Gecko-Inspired Adhesives that presents the first gecko-inspired adhesive that matches both the attachment and self-cleaning properties of gecko’s foot on a smooth surface.
Using glass microspheres to simulate contamination the scientists created a synthetic gecko adhesive that could self-clean and recover lost adhesion. Real world applications of self-cleaning adhesives are reusable adhesive tapes, clothing, medical adhesives (bandages) and pick-and-place robots, among others.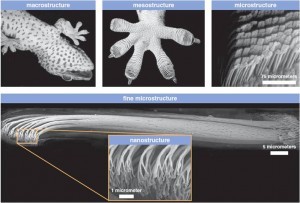
Everyday challenge with traditional adhesives is that they loose their stickiness once contaminated. Geckos have been intriguing researchers for decades because of their unique and striking capability to maintain the stickiness of their toes through contact self-cleaning. They can travel up the walls and ceilings in a wide variety of “dirty” settings retaining adhesion.
Upon experimentation, scientists discovered that the critical variable is the relative size of microfibers that make up the adhesive compared to the diameter of contaminant particles. Glass microspheres were used in diameters from 3 to 215microns. Glass microspheres were packed in air and used as supplied. Contamination of the samples was achieved by brining each sample in contact with a monolayer of glass microspheres with specific speeds under predetermined compressive loads. The cleaning process involved a load-drag-unload procedure.
Best self-cleaning results were obtained with the largest contaminants (glass microspheres), with the size of the adhesive fiber much smaller than the contaminating particle. This information is important to know when designing self-cleaning adhesives—make the adhesive fibers much smaller for improved adhesion recovery. This cleaning mechanism requires unloading particles by dragging. The other extreme of contaminating microspheres being much smaller than the adhesive fibers has advantages in some situations, even though it works by a different mechanism. Smaller microspheres tended to become embedded into the adhesive material. Particle embedding is a temporary cleaning process but might be sufficient in some applications.
FROM:microspheres.us
Posted by admin on February 3, 2016 at 1:22 am under Microspheres.
Comments Off on Glass Microspheres Used in Studying Self-Cleaning Gecko-Inspired Adhesives.
Optical glass beads, as a new product in the glass industry. It has a certain chemical stability, mechanical strength, electrical insulation and be rounded, uniform, and good liquidity.Its most unique properties with the original glass transparency, with the return of retroreflective performance. Especially the use of different conventional glass raw material of high refractive index glass beads much broader range of applications than the ordinary type beads, in addition to serving highways and airports and all kinds of road marking paint sign board outside,Can also be made reflective clothing, reflective rain gear, a traffic policeman on duty at night with reflective sleeves, etc. It can greatly reduce traffic accidents at night or in rain and fog days. Early in the 1960s the US government to develop a “federal highway regulations” provides highway lane, traffic signs, road signs, road signs and so on.In the headlights illuminated necessary to achieve the standard luminous indicators improve visibility distance traffic signs, the need to adapt to the highway. That this is to reduce traffic accidents most cost-effective way.”International maritime rescue organization” has also been stipulated that all vessels with a life buoy, life jackets and all life-saving equipment and the corresponding buoy flags are required glyphs reflective material with a high refractive index glass beads made.Helicopters and lifeboats to sea only available light to detect targets at night and rain and fog days in the rescue time and space. So that in addition, the use of high refractive index glass microspheres made of other reflective materials are also widely used in other industries, for example: large oil derrick, tower, movie screen, large public spaces such as billboards.
Posted by admin on January 29, 2016 at 9:30 am under Uncategorized.
Comments Off on Optical glass beads.
Summary:
K20 glass bubbles have a density of 0.2 g/cc and an isostatic crush strength of 500 psi.
Properties:
Lower viscosity, improved flow
Increased filler loading, reduced cost
VOC reduction
Chemical stability and inertness
Reduced dielectric constant
Thermal conductivity reduction
Temperature resistance
Applications:
Mining
Paints and coatings
Insulation and buoyancy
Transportation
from: palmerholland
Posted by admin on January 22, 2016 at 5:24 am under glass bubble.
Comments Off on K20 GLASS BUBBLES.
 Glass Bubbles are engineered hollow glass spheres that
Glass Bubbles are engineered hollow glass spheres that
can be used as a density reducing additive.
Used for drilling fluids/cement slurries to reduce
and control bottom hole pressure.
This article comes from 3M Edit Post
Posted by admin on January 15, 2016 at 2:04 am under glass bubble.
Comments Off on Glass Bubbles for Cementing and Drilling Fluids.
Thermal conductivity measurements were performed to determine the characteristics of hollow glass microspheres as an insulating material and as an opacifying agent for other insulations. The experiments were carried out with a radial flow heat transfer apparatus especially designed to suppress extraneous heat transfers, both internal and external to the heated section, and to provide uniform temperatures on the bounding surfaces. Three types of microsphere insulations were investigated, differing in bulk density and in the presence or absence of an aluminizing coating. The thermal conductivity of the microsphere insulations was found to be about one and a half times that of stagnant air over a wide temperature range. Additional experiments, involving the use of an opacifier (powdered silicon), demonstrated that radiative transfer has a minor effect on the thermal conductivity of microsphere insulations. This finding was corroborated by the fact that the high-temperature conductivity of the aluminized microspheres was not appreciably different from that of the uncoated microspheres. Another set of experiments was performed in which microsphere insulation was added to opacify silica aerogel, a fine powder insulation that is markedly affected by radiative transfer. The presence of the microspheres brought about reductions in conductivity of almost a factor of two at an optimum mixture ratio of the constituents. Furthermore, it was found that the conductivity of such a mixture was lower than that of either constituent, thereby illustrating their synergistic interaction.
Copyright © 1976 by ASME
Posted by admin on January 9, 2016 at 5:24 am under Hollow Glass Microspheres.
Comments Off on Characteristics of Hollow Glass Microspheres as an Insulating Material and an Opacifier.

They offers unique capability to manufacture microspheres and micro-particles with partial coatings and dual functionality. Currently half-shell or hemispherical coatings can be applied to any sphere (glass, polymer, ceramic) in sizes 45 micron in diameter on up to 1mm and higher. Hemispherical coatings of less than 1 micron with tolerances as low as 0.25 micron have been routinely demonstrated. Color combinations are truly unlimited. White, black, silver, blue, green, red, yellow, brown, purple in both fluorescent and non-fluorescent have been made. Sphericity of greater than 90% and custom particle size ranges are offered.
The custom coating capability offers customers the ability to create fluorescent glass micro-spheres of the specific size and emission/excitation needed. As the micro spheres and coating are solvent resistant they work ideally as fluorescent tracers or highly visible targets. We can overcoat clear glass or silver coated glass for the effect needed.
For those needing very large Spheres can coat spheres of 1 mm and larger.
The microparticles are now available as either dry powder or in a dielectric oil.
From:Microspheres Online
Posted by admin on December 29, 2015 at 3:04 am under Microspheres.
Comments Off on The microparticles are now available as either dry powder or in a dielectric oil.
Glass microspheres are microscopic spheres of glass manufactured for a wide variety of uses in research,medicine, consumer goods and various industries. Glass microspheres are usually between 1 to 1000 micrometers in diameter, although the sizes can range from 100 nanometers to 5 millimeters in diameter. Hollow glass microspheres, sometimes termed microballoons, or glass bubbles have diameters ranging from 10 to 300 micrometers.
Hollow spheres are used as a lightweight filler in composite materials such as syntactic foam and lightweight concrete. Microballoons give syntactic foam its light weight, low thermal conductivity, and a resistance to compressive stress that far exceeds that of other foams. These properties are exploited in the hulls of submersibles and deep-sea oil drilling equipment, where other types of foam would implode. Hollow spheres of other materials create syntactic foams with different properties, for example ceramic balloons can make a light syntactic aluminium foam.
Hollow spheres also have uses ranging from storage and slow release of pharmaceuticals and radioactive tracers to research in controlled storage and release of hydrogen. Microspheres are also used in composites to fill polymer resins for specific characteristics such as weight, sandability and sealing surfaces. When making surfboards for example, shapers seal the EPS foam blanks with epoxy and microballoons to create an impermeable and easily sanded surface upon which fiberglass laminates are applied.
Glass microspheres can be made by heating tiny droplets of dissolved water glass in a process known as ultrasonic spray pyrolysis (USP), and properties can be improved somewhat by using a chemical treatment to remove some of the sodium. Sodium depletion has also allowed hollow glass microspheres to be used in chemically sensitive resin systems, such as long pot life epoxies or non-blown polyurethane composites
Additional functionalities, such as silane coatings, are commonly added to the surface of hollow glass microspheres to increase the matrix/microspheres interfacial strength (the common failure point when stressed in a tensile manner).
Microspheres made of high quality optical glass, can be produced for research on the field of optical resonators or cavities.
Glass microspheres are also produced as waste product in coal-fired power stations. In this case the product would be generally termed “cenosphere” and carry an aluminosilicate chemistry (as opposed to the sodium silica chemistry of engineered spheres). Small amounts of silica in the coal are melted and as they rise up the chimney stack, expand and form small hollow spheres. These spheres are collected together with the ash, which is pumped in a water mixture to the resident ash dam. Some of the particles do not become hollow and sink in the ash dams, while the hollow ones float on the surface of the dams. They become a nuisance, especially when they dry, as they become airborne and blow over into surrounding areas.
Posted by admin on December 26, 2015 at 7:36 am under Microspheres.
Comments Off on Glass microspheres are also produced as waste product in coal-fired power stations.
Sinosteel Maanshan Institute of Mining Research Co., Ltd., established in 1963 and directly subordinate to the former Ministry of Metallurgical Industry, is a large comprehensive research and development institution in China’s metallurgical mine field. We are one of the units approved early by the Academic Degree Awarding Committee of the State Council to have independent right to award the master academic degree and one of the units approved by the State Economic and Foreign Trade Ministry to have the right to import and export products. Our firm developed into a scientific and technological enterprise in 1999 and now belongs to China Sinosteel Group.
Sinosteel Maanshan Institute of Mining Research Co., Ltd. is a National Torch Program High-tech Enterprise. Our firm has outstandingly completed a series of major national scientific and technological projects, including “the Sixth Five-Year Plan” and “the Eleventh Five-Year Plan”, and published over 2,500 academic papers at home and abroad. Our firm has more than 1,700 sets of all kinds of equipment and facilities and over 50 supporting pilot plants. Sinosteel Maanshan Institute of Mining Research Co., Ltd. cooperates with Chinese Academy of Sciences to develop an industrialized technique to produce high-performance hollow glass microspheres, filling a gap at home.
Sinosteel Maanshan Institute of Mining Research Co., Ltd. is located in Maanshan — known as the National Civilized City, the National Sanitary City and the National Garden City. Maanshan is described as “a Branch of Flower along the Yangtze River”. The hollow glass microsphere company (subsidiary of Sinosteel Maanshan Institute of Mining Research Co., Ltd.,) covers an area of 20,000m2, with several large-scale standard plants totally up to 10,000m2 and integrated modern office buildings of 7,000m2. Our company has obtained ISO9001:2000 quality management system certificate. In the fierce market competition, our company holds the business spirit of “quality, honesty, good service” and relies on advanced technology and strong strength to provide customers with better products and services.
Posted by admin on December 18, 2015 at 7:38 am under Uncategorized.
Comments Off on Sinosteel Maanshan Institute of Mining Research Co., Ltd..



